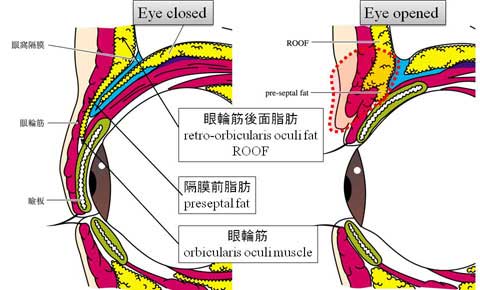
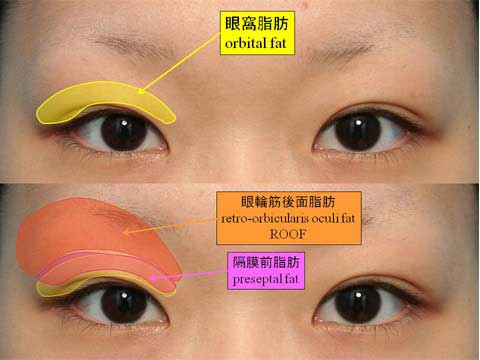
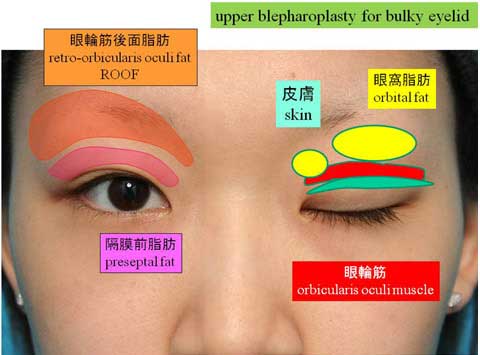
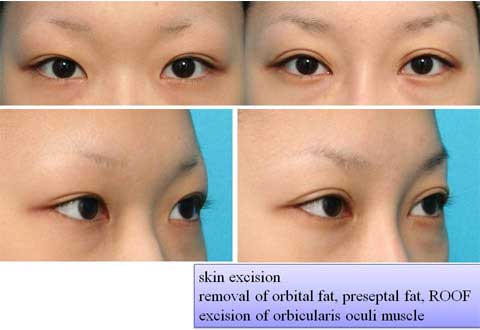
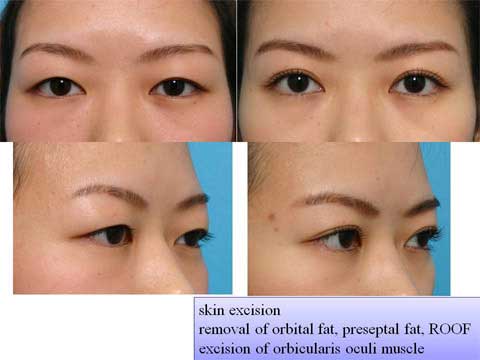
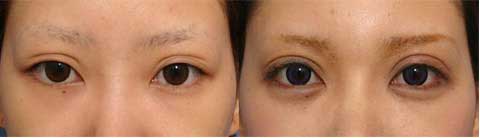
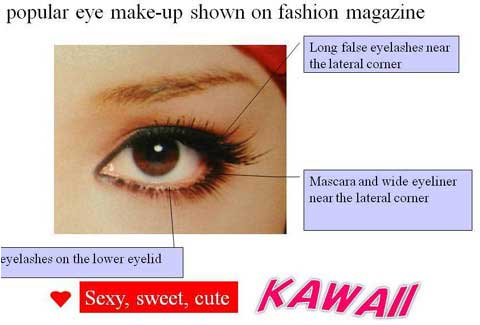
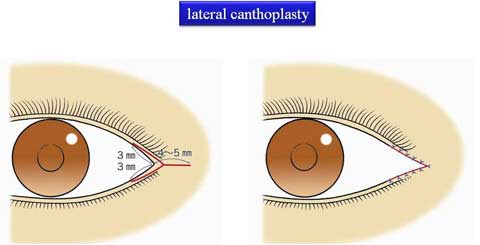
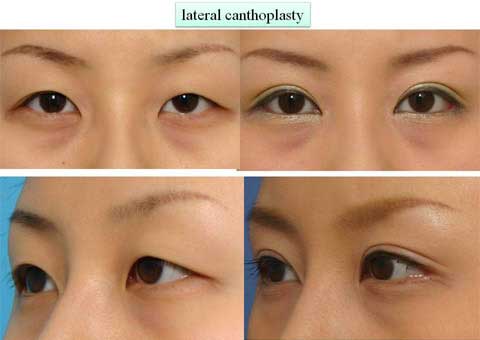
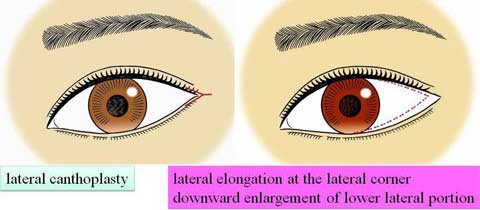
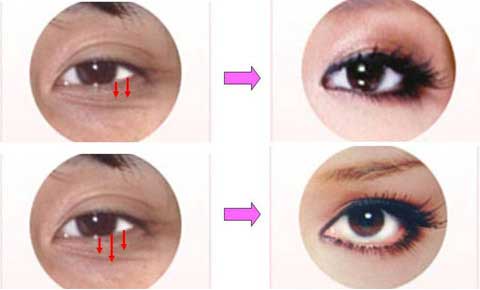
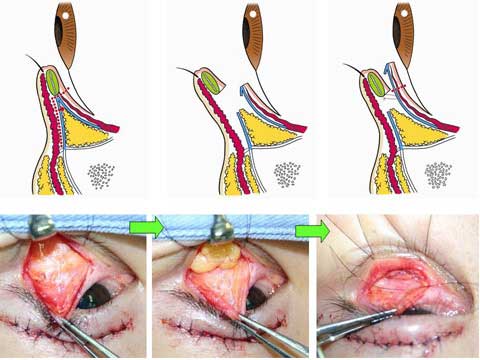
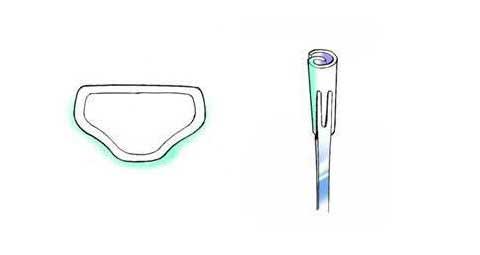
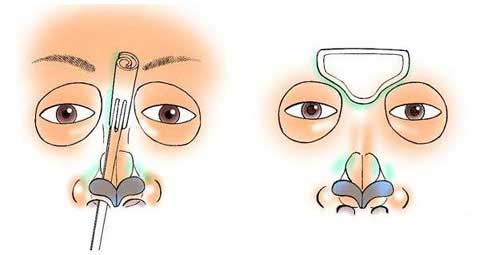
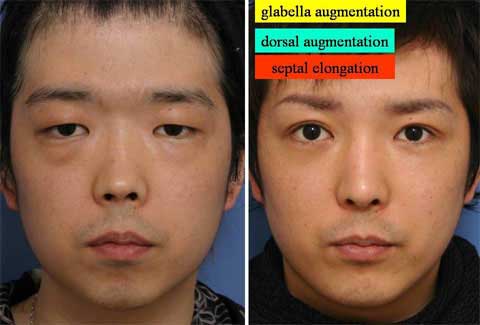
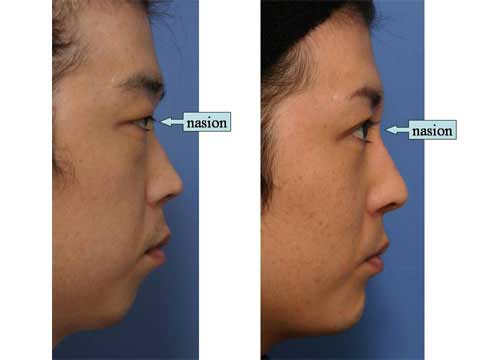
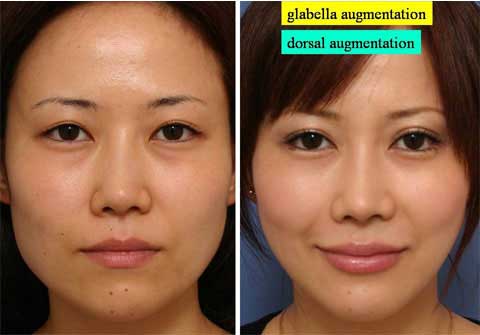
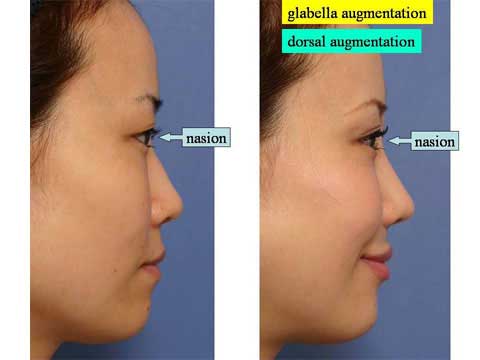
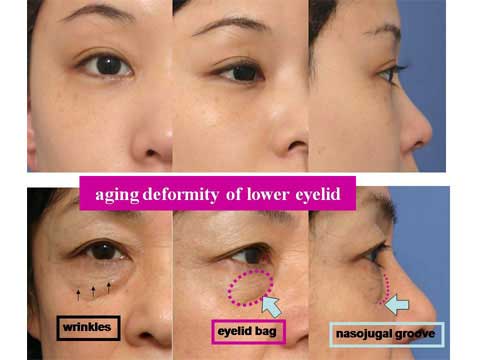
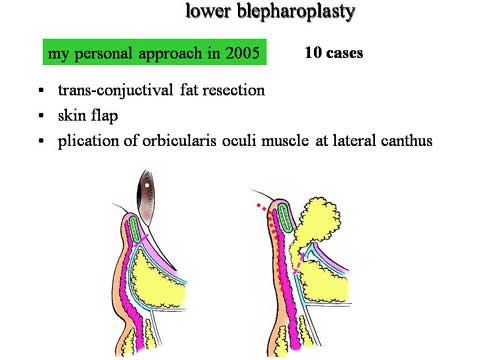
第1回低侵襲形成美容外科学会、ソウル、韓国 2009/09/4-6
1st International Congress of Minimal Invasive Plastic Surgery-seoul-2009/09/4-6
General subject :
Stitch method for correction of acquired blepharo-ptosis
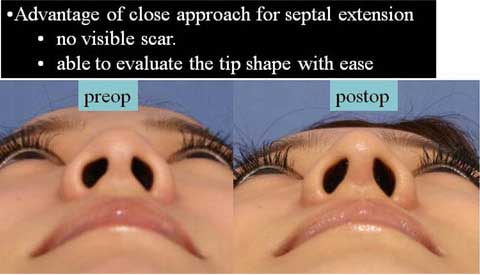
Spindle skin excision to correct Polly beak deformity in rhinoplasty
Education lecture :
Treatment of retaining ligament, SMAS and fat tissue in facelift
Announcement contents :
1. Stitch method for correction of acquired blepharo-ptosis
: Keizo Fukuta, M.D.
Verite Clinic, Tokyo Japan
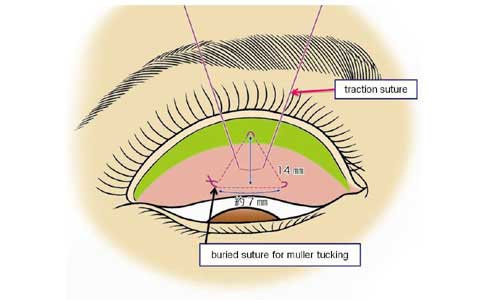
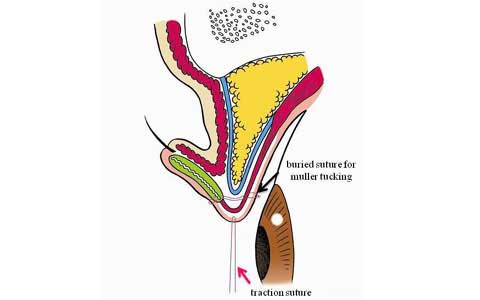
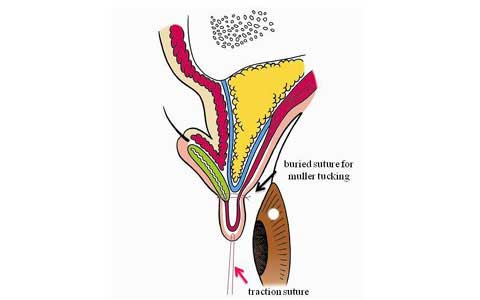
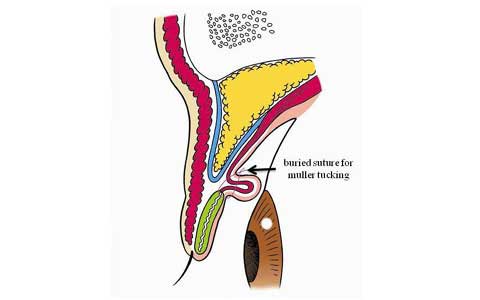
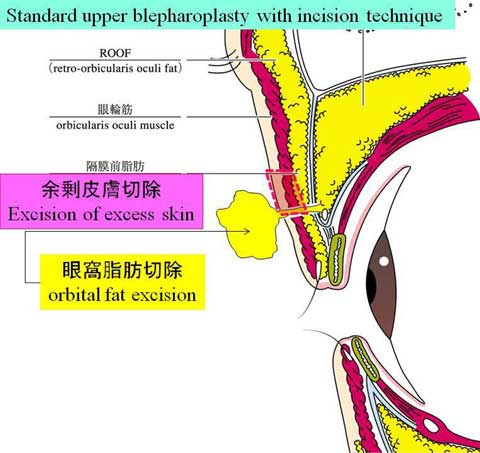
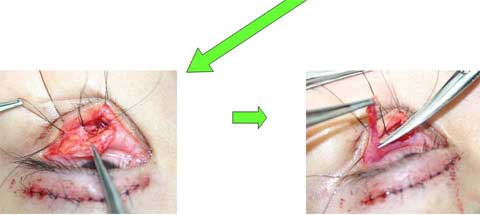
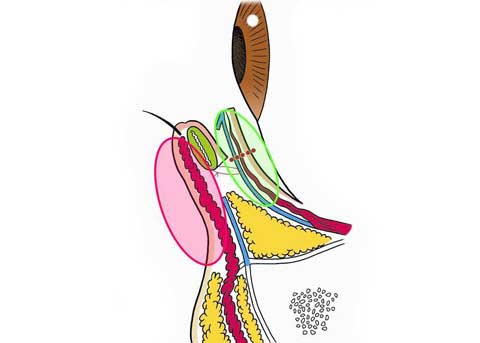
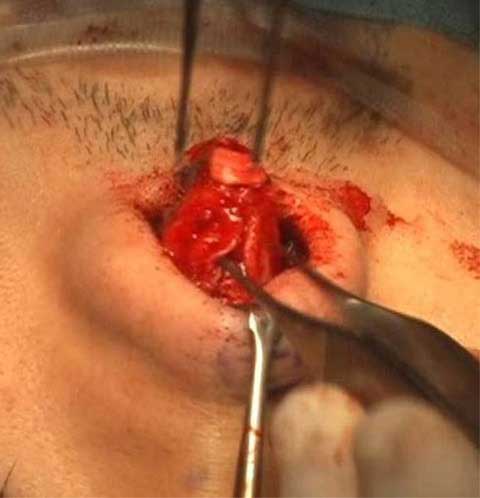
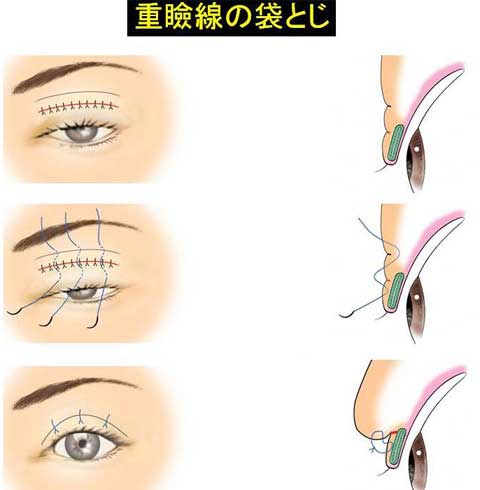
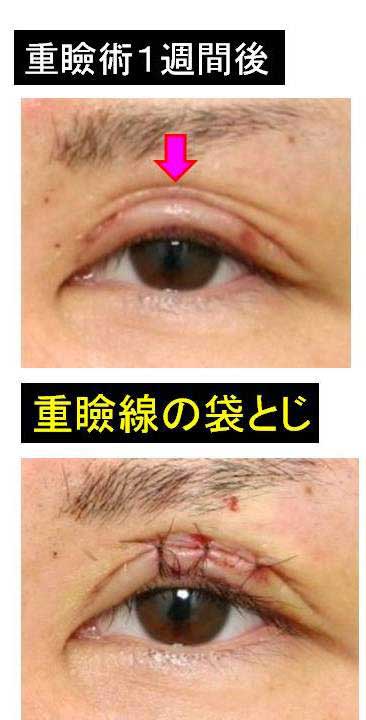
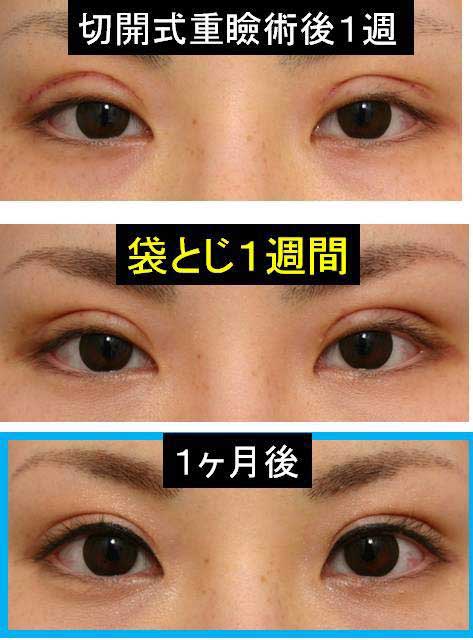
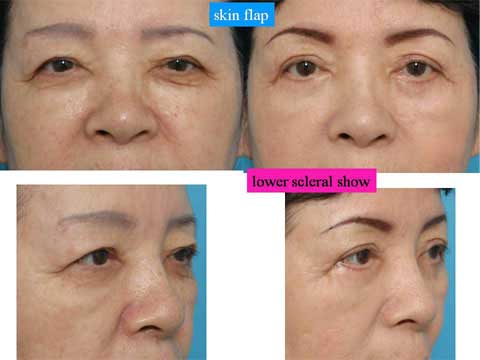
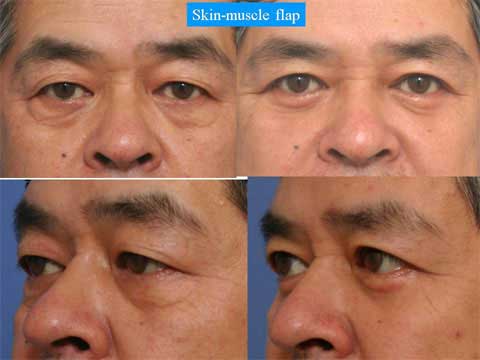
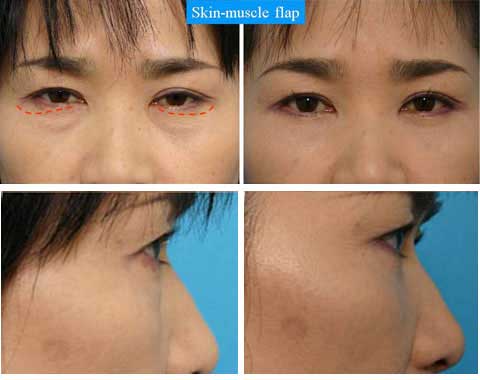
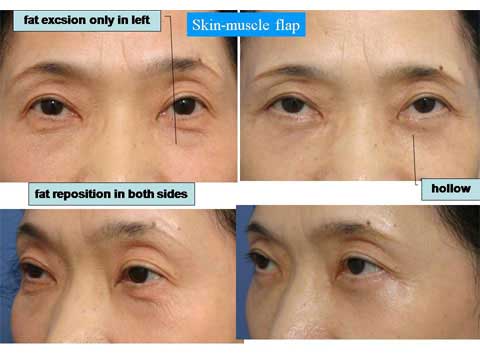
This paper presents the use of stitch technique to correct acquired blepharo-ptosis without any incision.
7-0 nylon suture is buried under the conjunctiva between the upper margin of tarsus and the upper sulcus in a triangular fashion.
The ligation of the suture shortened the conjunctiva and Muller muscle longitudinally.
The vertical distance of the conjunctiva to be plicated is 14 mm in many of cases, but needs be changed for each case.
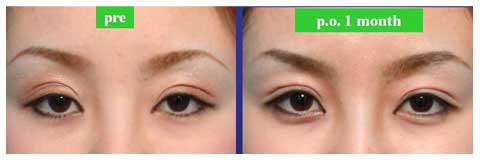
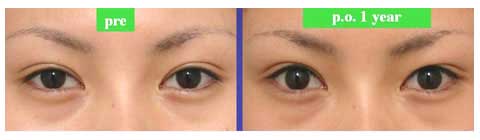
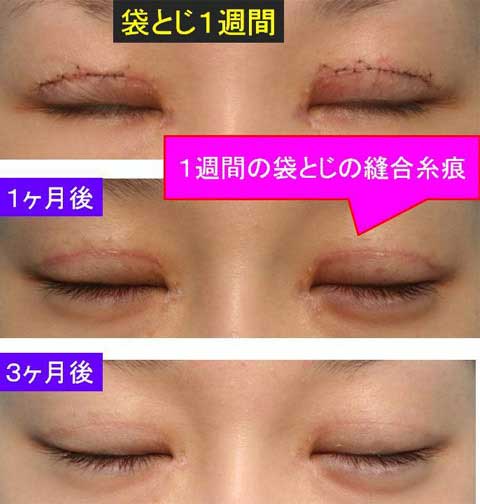
Although long term result is still unclarified, follow-up of some of my cases has revealed the lasting of ptosis correction for 3 years.
This procedure was found useful to correct asymmetry of ptosis after levator aponeurosis repair via incisional approach.
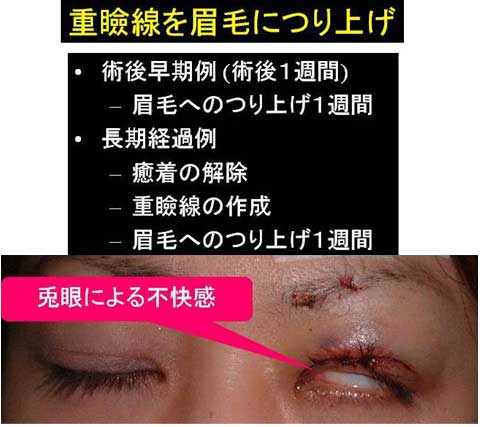
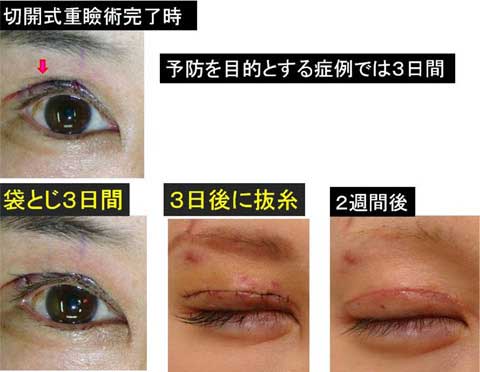
The swelling after the stitch ptosis correction is mild in most of cases.
Other possible complications are ecchymosis, asymmetry over-correction or under-correction.
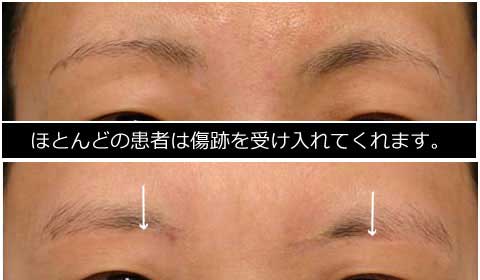
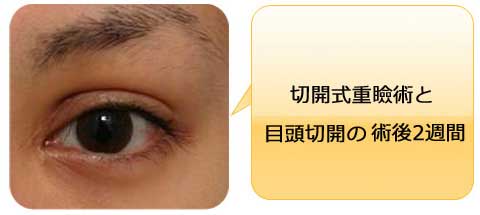
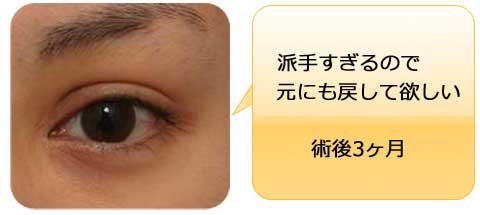
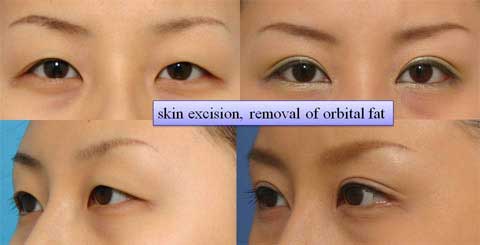
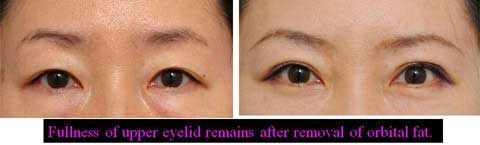
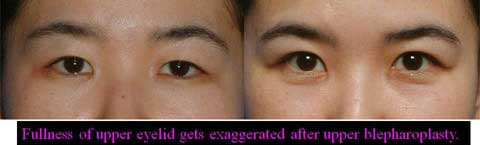
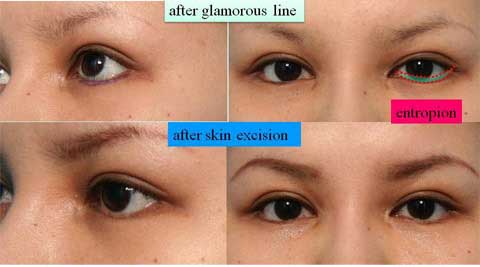
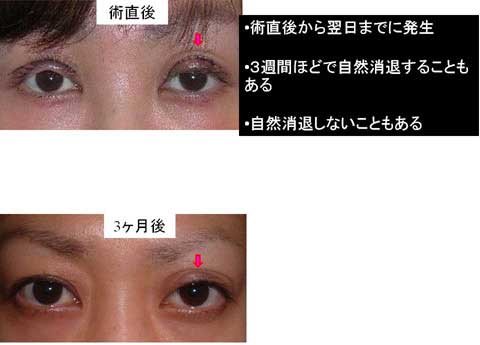
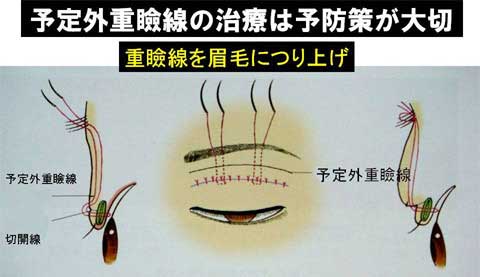
The width of double fold became narrower after the ptosis repair.
Stitch upper blepharoplasty was therefore performed depending of the patients’ request simultaneously or subsequently.
2. Spindle skin excision to correct Polly beak deformity
in rhinoplasty
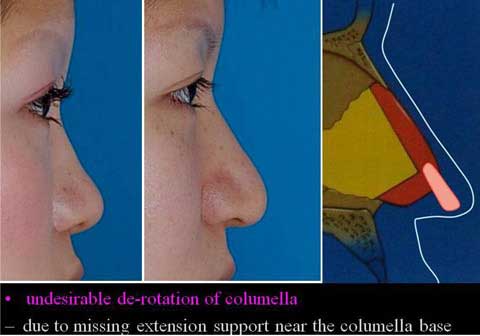
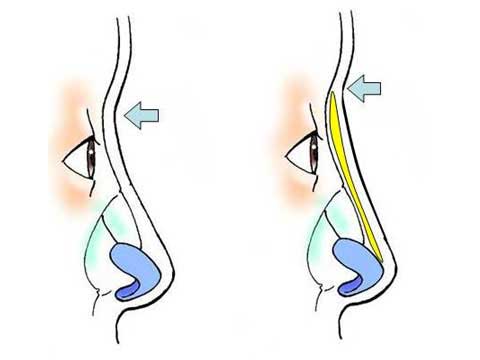
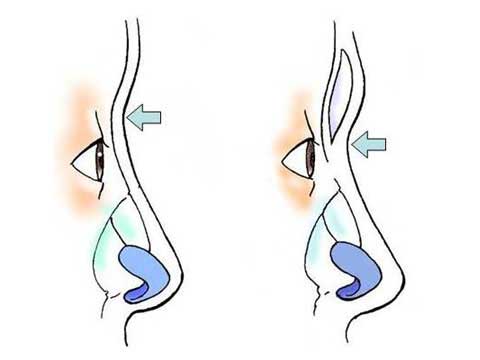
Polly beak deformity is post-rhinoplasty deformity associated with fullness in the supratip.
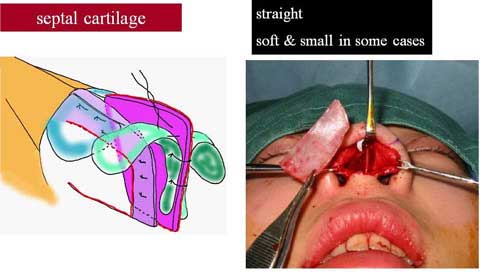
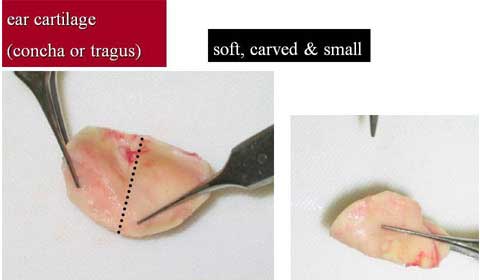
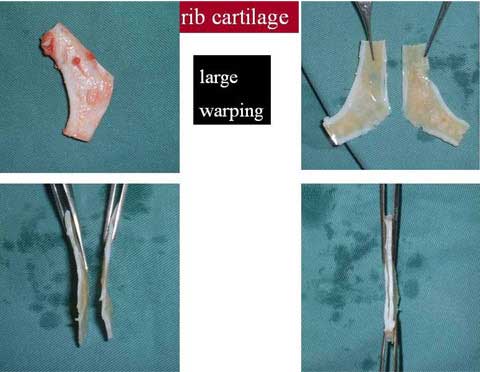
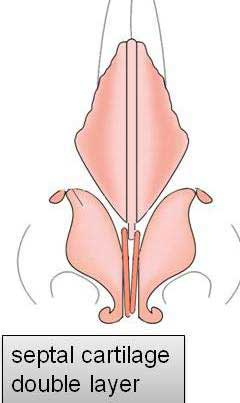
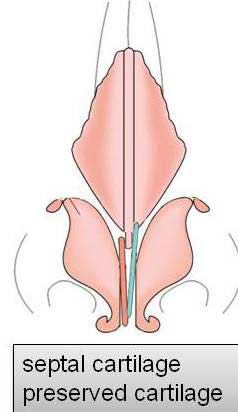
Two categories of a Polly beak deformity are generally described; cartilaginous source and soft tissue source.
The letter category is more common in Orientals and more difficult to correct.
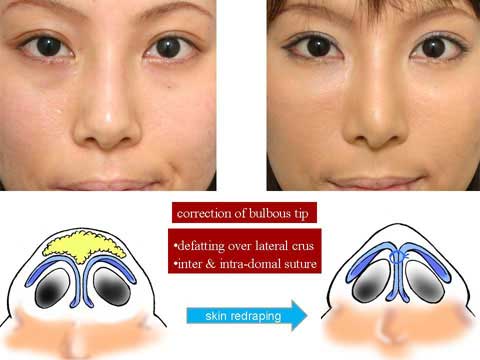
The nasal skin in many of Oriental patients is thick and inelastic, providing poor redraping after reduction rhinoplasty such as correction of bulbous tip.
Excess of thick skin and soft tissue develops at the supratip region.
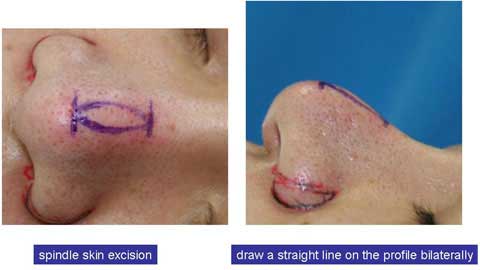
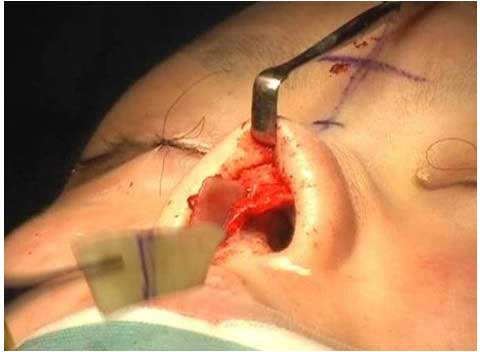
I have used direct skin excision in a spindle shape overt the Polly beak deformity.
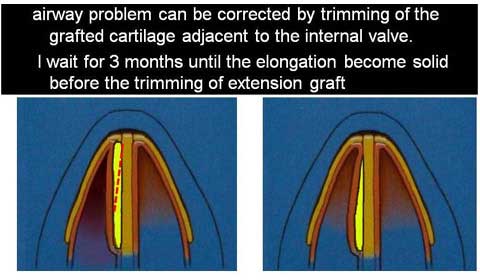
This simple procedure can remove the excess soft tissue and convert the bulging dorsal contour to straight line.
Only problem concerned after this method is a postoperative scar on the nasal dorsum.
7 Japanese patients were treated with the direct excision.
The scar became inconspicuous in 2 cases without further treatment and in 5 cases after CO2 laser abrasion.
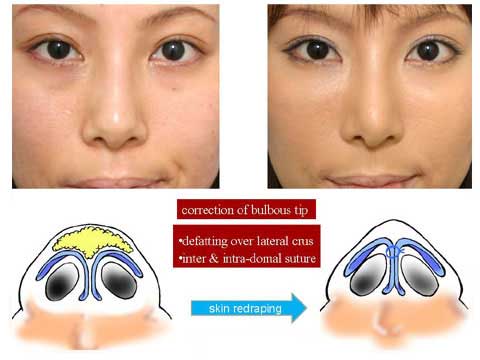
The correction of bulbous tip, making the tip narrow and sharp, is a common request for Oriental rhinoplasty.
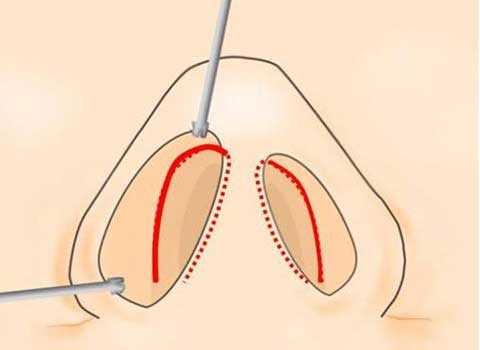
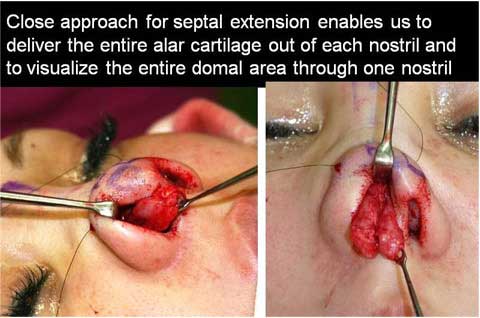
The correction can be done using endo-nasal incision by removing subcutaneous fat tissue over the lateral crura of alar cartilage and intra and inter domal suture.
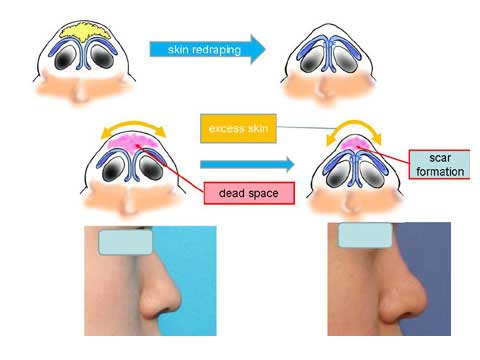
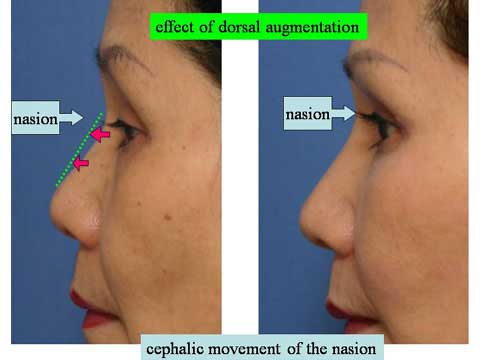
Why does Polly beak deformity occur?
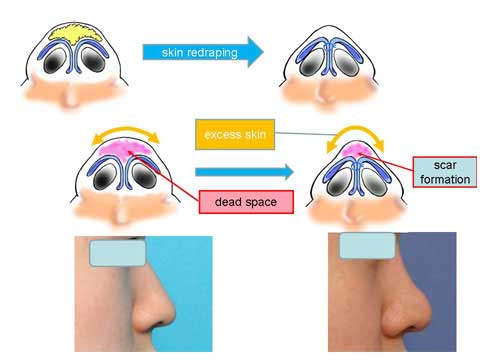
When we perform the defatting and cartilage suture, we expect that the skin should redrape nicely over the modified cartilagenous structure.
In case the skin is soft and pliable, it will do so.
However, those who ask for bulbous tip correction, their skin tends to be thick and hard.
The nice redraping does not take place.
Therefore, the dead space from wide subcutaneous dissection can not be eliminated, causing scar tissue formation.
Excess amount of skin will bulge out when it is squeezed in the midline.
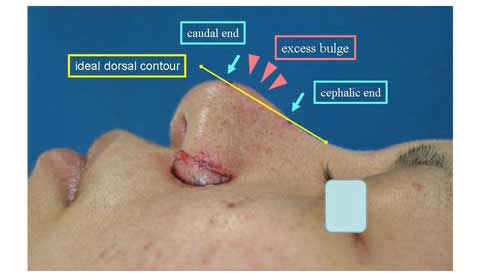
A case with Polly beak deformity after having undergone the correction of bulbous tip.
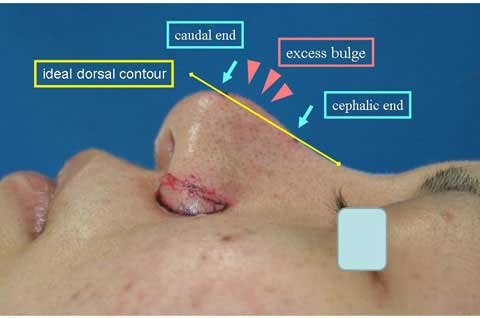
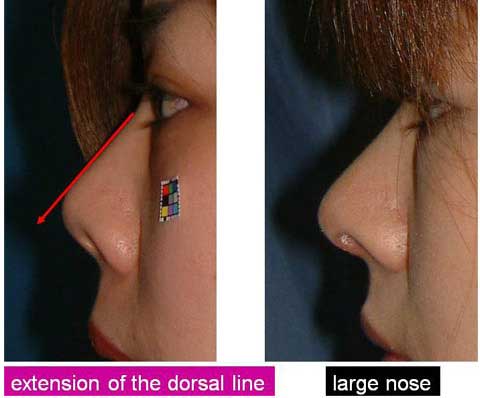
Here in my imagination, I extend a dorsal contour line in straight.
This line helps me to find the caudal end and cephalic end of the excess bulge.
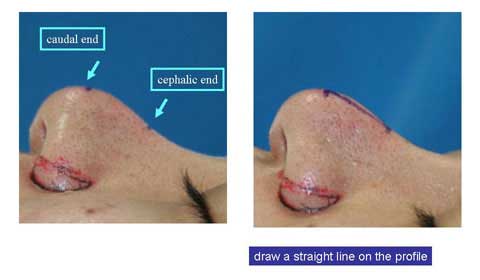
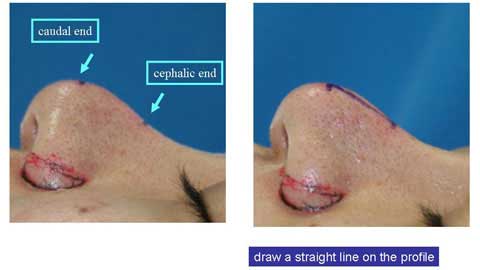
Now I draw a straight line from the cephalic end point to the caudal end point on the profile.
I draw another line on the other side.
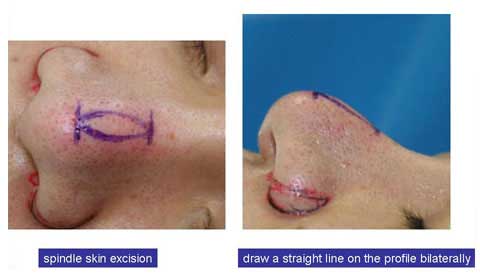
When we look from the front, those straight lines are not really straight but slightly curved.
We can actually see a marking of spindle shape.
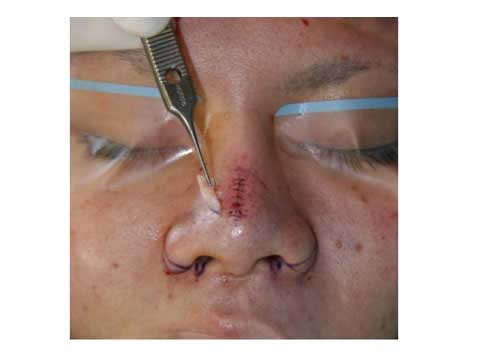
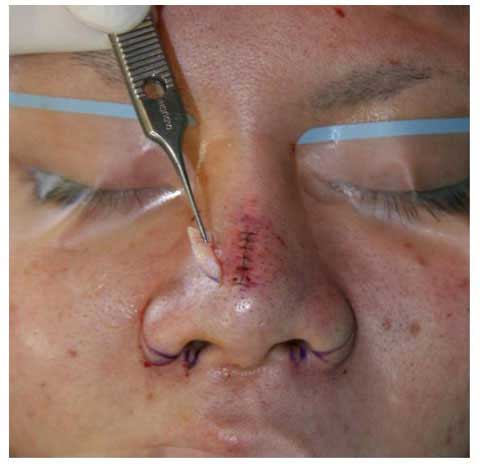
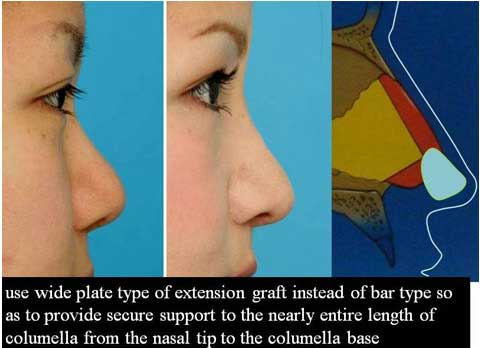
I excised full thickness skin of the spindle mark and closed the defect in two layers.
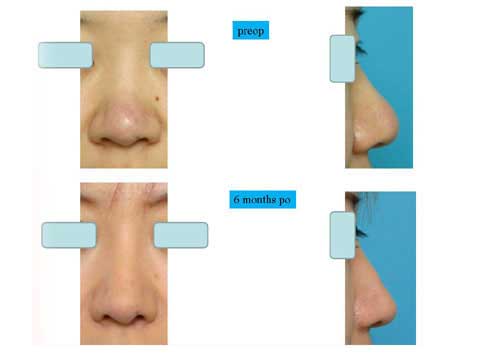
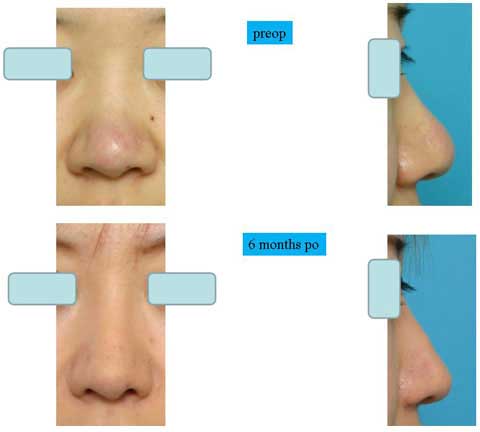
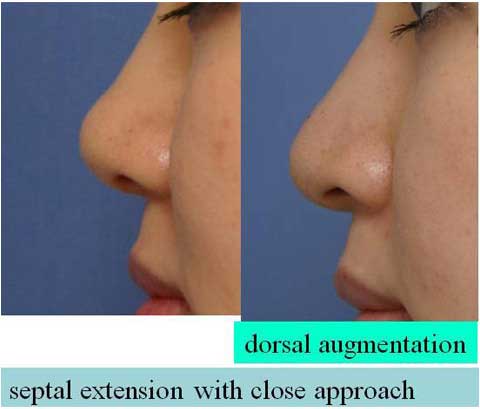
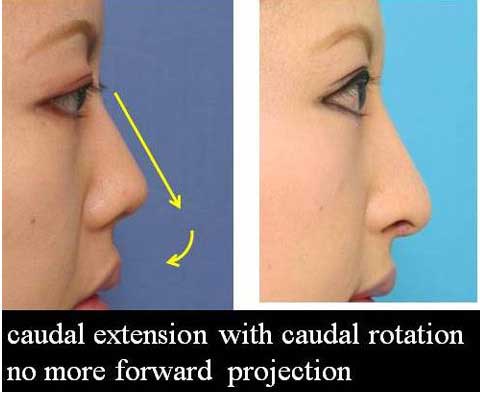
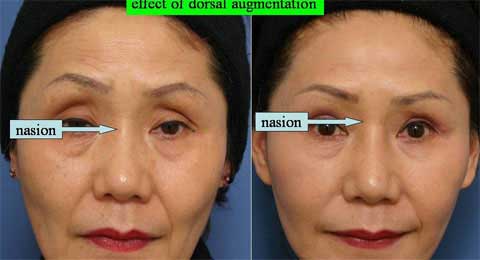
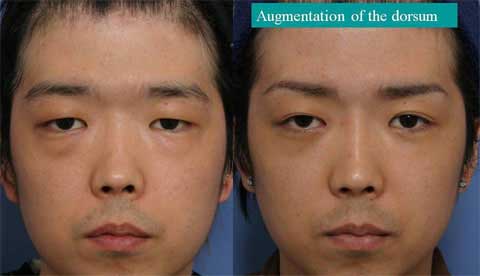
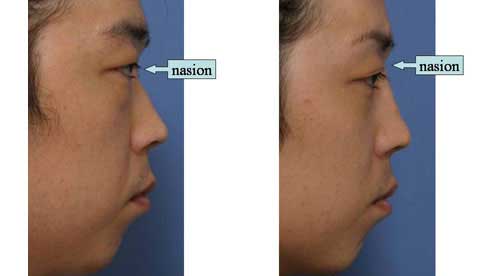
These are the patient before surgery.
This is the result 6 months after skin excision.
The bulging of the supratip region became flat, even concave. The scar is inconspicuous.
In summary, spindle skin excision is very effective to correct Polly beak deformity.
Although this procedure leaves a scar, the scar is well accepted by patients.
Actually the scar was almost invisible in some cases.
This procedure was found useful not only for postoperative Polly beak deformity but also for primary bulky tip.
The amount of skin excision should be conservative in width, otherwise it will result in concave contour or dog ear deformity.
3. Treatment of retaining ligament, SMAS and fat tissue in facelift
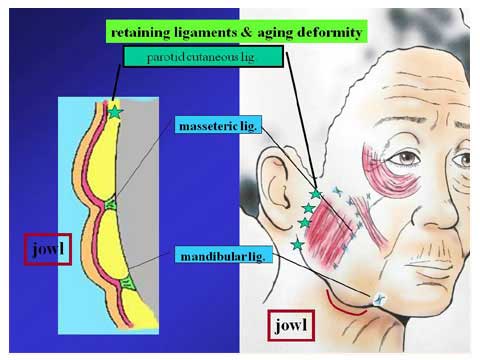
The retaining ligaments suspend the facial skin to the underlying deep structure.
As aging, the soft tissue (skin and subcutaneous fat) looses the firmness.
The skin between the masseteric retaining ligament and mandibular retaining ligament show the sag over the mandibular ligaments due to gravity in the upright position.
This sagging deformity is recognized as jawl.
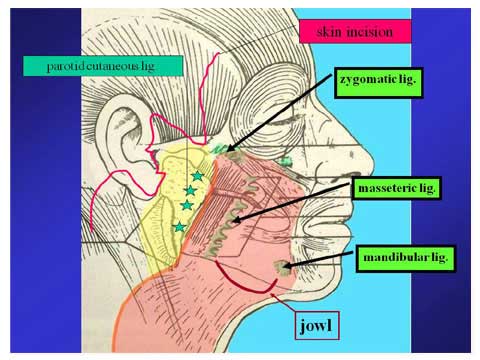
A long skin incision is made along the temporal hairline, the side burn, natural crease in front of the ear, the ear lobe, postauricular groove and occipital hairline.
The lateral margin of platysma and muscular portion of SMAS is located at 3 cm from the ear lobe.
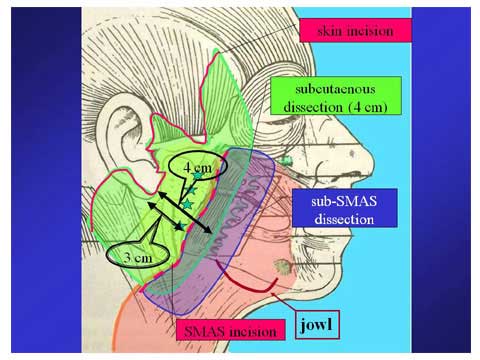
The subcutaneous dissection is made up to 4 cm from the ear lobe.
The SMAS is incised at the lateral margin of the platysma which is at 3 cm from the ear lobe.
The deep dissection is carried out under the SMAS and platysma and continued up to beyond the anterior margin of the masseteric muscle where the masseteric ligaments are present.
This sub SMAS dissection can release all the masseteric ligament s and zygomatic ligaments from the SMAS, which allow us to pull the medial portion of the skin and SMAS with traction of the SMAS flap.
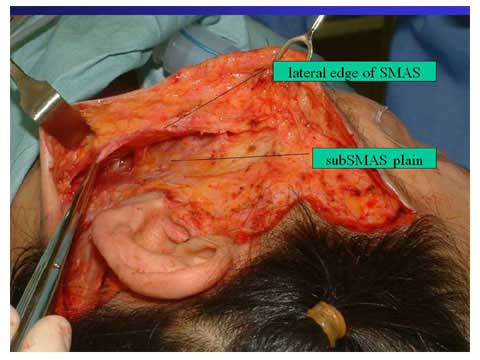
The intraoperative photo showing the 1cm long SMAS cuff attached to the skin flap and wide sub-SMAS pocket.
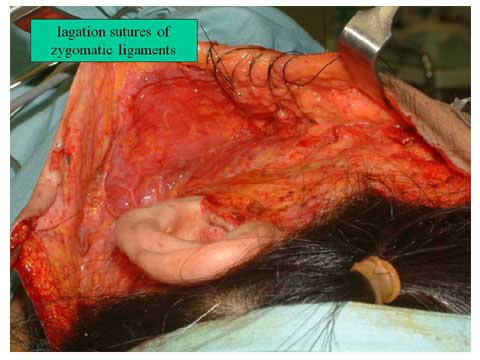
The suspension of the short SMAS flap to the mastoid fascia and relatively immobile SMAS over the parotid gland.
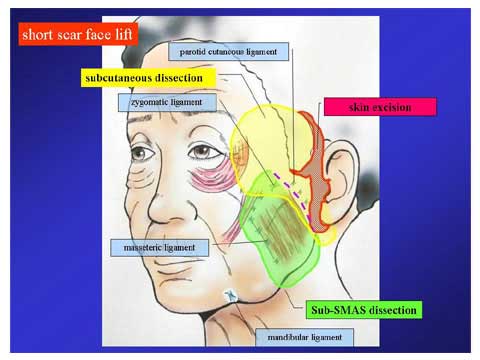
In case of no significant neck sagging, the facelift with a short scar is feasible.
This procedure eliminates an incision along the occipital hairline.
Instead of using the temporal hairline incision, an incision is made in the hair-baring skin the temporal area.
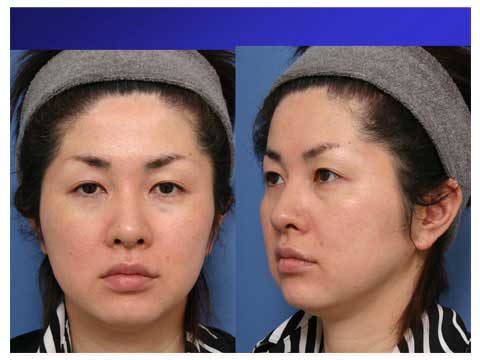
A 42 year old female presented with mild jawl deformity and heavy look in the upper eyelid.
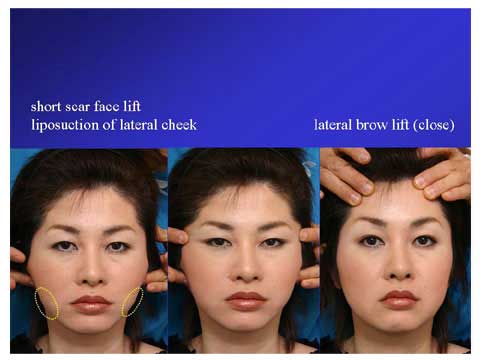
For her preoperative planning, traction of skin in front of the ear with fingers demonstrates the possible result from the short scar facelift.
The simulation shows budging in the lateral cheek in spite of the strong pull.
In order to make smaller the bulge which will remain after facelift alone, the combination of liposuction with facelift is useful.
The middle picture shows the simulation of facelift with temporal lift, which make the lateral canthus look sharper.
The patient denied to have temporal lift.
The right picture demonstrates possible result from lateral brow lift.
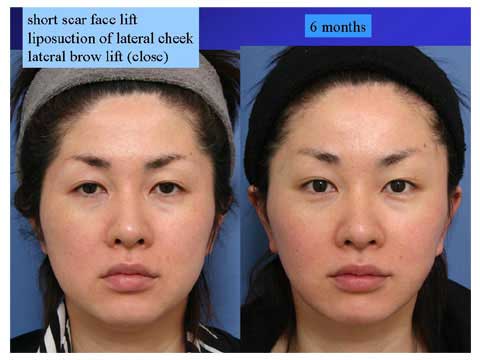
6 months after the short scar facelift with liposuction in the lateral cheek and lateral brow lift with close approach.
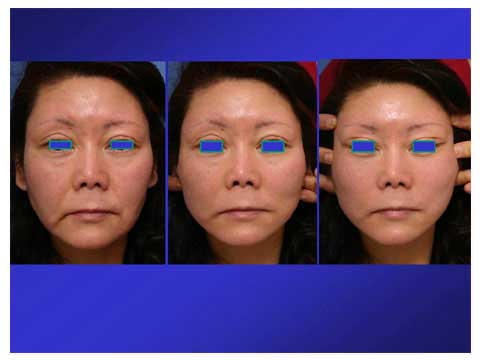
62 year-old female presented with jawl, marionette line, nasolabial fold and loss of soft tissue fullness.
The middle picture shows simulation of facelift for the lateral cheek.
The right picture shows simulation of facelift and temporal lift which provide the lateral canthal region and lower eyelid with pull in the super-lateral direction.
The patient chose to have temporal lift with pulled appearance of the lateral canthus.
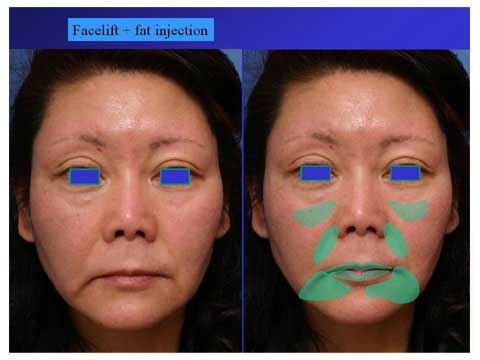
The green marking demonstrates the area for which lipofilling is planned.
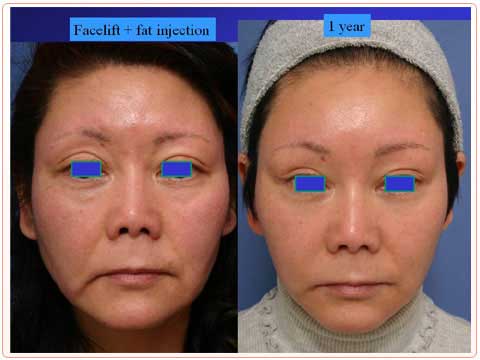
One year after facelift and temporal lift with lipo-injection.